
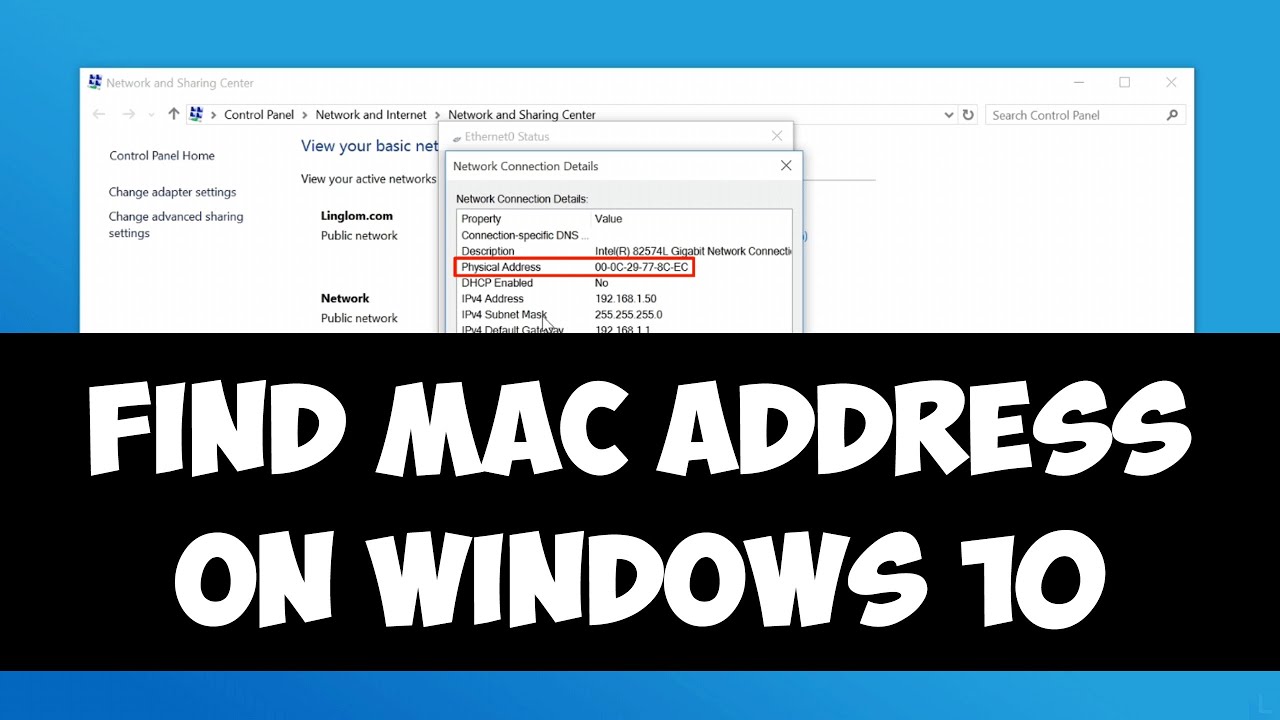
Understanding how network traffic is forwarded and received by the MAC address, understanding MAC address assignment is important to Because all Layer 2 traffic decisions are based on an interface’s MAC addresses are used to identify network devices at LayerĢ. Regarding MAC address assignments in a Virtual Chassis, see Understanding MAC Address Assignment Standalone Juniper Networks EX Series Ethernet Switches. This topic describes MAC address assignment for interfaces on DHCPĪlso typically uses MAC addresses when assigning IP addresses to nodes. Of a node using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table. IP networks maintain a mapping between the IP and MAC addresses Whereas IP addresses change when the node moves from one part of the MAC addresses are typically fixed on a per-node basis,
#Mac address lookup on mac software
Node, whereas IP addresses apply to the software implementation of The difference is that the MAC addresses apply to a physical or virtual Which runs at Layer 3 (networking and routing).
#Mac address lookup on mac serial
The second half of a MAC address represents the serial numberĪssigned to the adapter by the manufacturer.Ĭontrast MAC addressing, which works at Layer 2, with IP addressing, These IDs are regulated by an Internet standardsīody. The first half of a MAC address contains the ID number of theĪdapter manufacturer. MAC addresses are usually written in one of these formats: A MAC algorithm acceptsĪs input a secret key and an arbitrary-length message to be authenticated,Ī MAC address is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (48 bits in long). That are assigned to all ports on a switch. Identify one another at the data link layer, by using the MAC addresses In Layer 2, multiple devices on the same physical link can uniquely This channel may provide unicast, multicast, The MAC sublayer emulates a full-duplex logical communication channel The MAC sublayer acts as an interface between the logical linkĬontrol (LLC) Ethernet sublayer and Layer 1 (the physical layer). Several terminals or network nodes to communicate in a network. Provides addressing and channel access control mechanisms that enable In Layer 2 of a network, the Media Access Control (MAC) sublayer This topic provides an introduction to the MAC sublayer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
